Cellulose Olivate Registered as a New Cosmetic Ingredient in China
The registration of new cosmetic ingredients in China poses challenges due to its complexity and unpredictability. Between 2004 and 2014, only 10 new ingredients gained approval. No new ingredients were approved from 2015 to 2020. The situation only shifted when the Cosmetic Supervision and Administration Regulation (CSAR) was implemented in 2021.
Under CSAR, cosmetic ingredients are stratified according to their inherent risks. High-risk ingredients like sunscreens, preservatives, colorants, hair dyes, and whitening agents require registration with the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). Lower-risk ingredients can be used after an approved notification process.
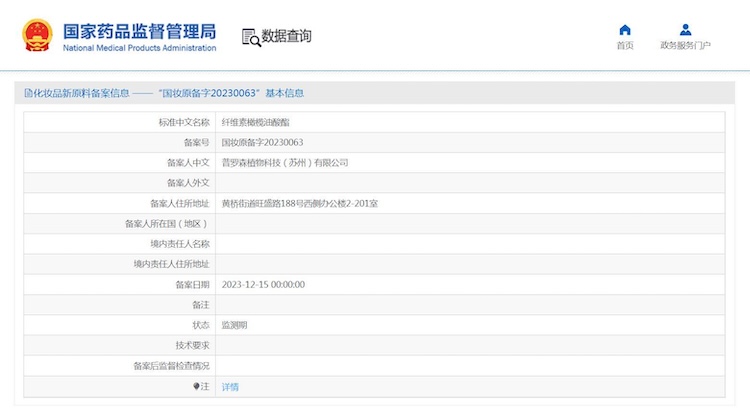
Post-CSAR, NMPA data shows that six new cosmetic ingredients achieved filing status in 2021, 42 new ingredients were successfully filed in 2022, and as of December 15, 2023, 63 new ingredients have obtained filing status. By achieving NMPA filing status for our new ingredient Cellulose Olivate, Proscien stands out as one of the few companies that has successfully gained the approval of a new cosmetic ingredient in China.
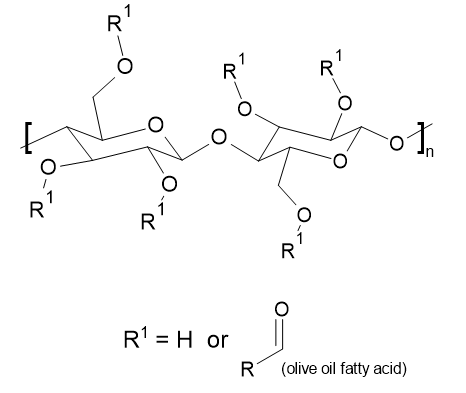
An innovative new product developed by Proscien's R&D team, Cellulose Olivate is a thickening, emulsifying ingredient derived entirely from natural raw materials. Suitable for all oil-in-water cosmetics, it forms lamellar liquid crystal structures, imparting viscoelasticity, delicate skin feel, and stability to formulations.
Cellulose Olivate is a new INCI name that was assigned to Proscien by PCPC in August 2023. To obtain an approval in China, we meticulously tested the product and prepared a dossier to meet NMPA's stringent requirements. Cellulose Olivate is now available in China as a unique cosmetic ingredient offered exclusively by Proscien.